Adjustment of individual vitamins and minerals
According to the latest scientific findings, the minimum and maximum amounts of nutrients are even more in line with the nutritional needs of infants.

*prices incl. VAT plus shipping costs
Ready to ship today,
Delivery time appr. 1-4 days²


HiPP Comfort special food, for dietary management of flatulence, lactose-related 3-month colic and constipation in infants.

What are LCPs?
LCP stands for "Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids" and describes long-chain,
polyunsaturated fatty acids. Among other things, these are very important for the development of brain and nerve cells and the baby's ability to see. Examples of LCPs include docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) - an omega-3 fatty acid - and arachidonic acid (ARA) - an omega-6 fatty acid.
Because babies cannot yet produce enough LCPs themselves in the first few months of life,LCPs arealready added to our specialty foods . Under the new EU directive on infant milk formula, the addition of DHA is now required by law.
Expert opinion favors the addition of both DHA and ARA to infant formula. Otherwise, it has been shown that there can be deviations in these fatty acids compared to breastfed infants, who are always supplied with ARA via breast milk. This is why we have been using the combination of DHA and ARA in our HiPP special foods for years.
What is DHA?
DHA - the abbreviation stands for docosahexaenoic acid - is a long-chain, polyunsaturated omega-3 fatty acid.
Why is DHA important?
Omega-3 fatty acids contribute to the normal development of brain and nerve cells and vision. Omega-3 fatty acids are naturally present in breast milk. To ensure that non-breastfed infants also have an adequate supply of DHA, DHA is added to infant formula, e.g. in the form of fish oil.
What is ARA?
ARA - the abbreviation stands for arachidonic acid - is a long-chain, polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid. Omega-6 fatty acids are naturally present in breast milk. Their content is strongly dependent on the mother's diet. To ensure that non-breastfed infants are also adequately supplied with these vital fatty acids, ARA is added to infant formula, e.g. in the form of vegetable oils, e.g. from Mortierella Alpina.
According to the latest scientific findings, the minimum and maximum amounts of nutrients are even more in line with the nutritional needs of infants.
As before, our special foods are adapted to the particular nutritional needs of infants. So your baby gets exactly what it needs for its development.
For 50 years, we have been putting all our care and experience into producing the best infant formula. So with our HiPP Comfort and HiPP Anti-Reflux milk formula, you can rely on long-established concepts developed by nutrition experts based on breast milk - building on the latest findings in milk nutrition research.
Nothing will change with regard to our step-by-step concept, the product names and the age recommendations.
*for lactose-related 3-month colic
| Filling quantity (weight): | 600g |
| baby food: | powdered formula, specialty foods |
| country of origin: | EU / non-EU Agriculture |
| milk-free products: | No |
| Products with organic ingredients: | No |
| age group: | from birth |
| gluten-free products: | Yes |
| Shipping weight: | 0,565 kg |
| Manufacturer: | Hipp |
| Dimensions HxWxD (approx.): | 202x126x85 mm |
| Made in: | EU (Germany) |
| product group: | Baby Formula, Special food Comfort |
| brand: | Hipp |
| further properties: | climate neutral |
| Label: | DAAB e.V. Allergen Management, FSC seal, klimaneutral |
| Target group: | Baby |
| Manufacturer address: | Hipp GmbH & Co. Vertriebs KG, Georg-Hipp-Str. 7, 85276 Pfaffenhofen (Ilm), Deutschland |
Manufacturer contact: Hipp GmbH & Co. Vertrieb KG, 85276 Pfaffenhofen

" Taking the baby into the limelight carries a great deal of responsibility, which is
why our organic products are of a very special quality and are GM-free according to the EU Organic Regulation. "
What began over 60 years ago with organic farming is practiced in all areas of the company: the careful use of the environment and natural resources, a respectful togetherness and the highest quality. All of these are requirements that HiPP has grown and that are closely associated with the name HiPP.
Sustainability as a corporate philosophy
Sustainability is the balanced balance between the three dimensions of ecology, economy and social issues. Sustainability is not a hot topic for HiPP. As a manufacturer of baby food, HiPP has special responsibility for future generations. HiPP has been committed to organic farming for 60 years and, as a pioneer, has shaped sustainable standards. Sustainability management keeps an eye on the company as a whole and the entire value chain. Long-term orientation of entrepreneurial activity, careful use of natural resources and social interaction are the key ethical principles followed by HiPP.
HiPP is "excellent"!
The involvement of HiPP has received many awards. The great trust of consumers and the public, which is documented in these recognitions, is both a great honor and a commitment for the baby food manufacturer. The company's claim is to continue meeting these expectations.
Since 2002, the Ökologia Prize has been awarded to companies or entrepreneurs who have committed themselves through particularly exemplary projects in favor of ecology and contributed to the realization of the desired ecological and social market economy. On October 19, 2017, Claus Hipp received the award from the Rhineland-Palatinate Minister of the Environment Ulrike Höfken in Mainz.
"From today's perspective, of course, many of what Claus Hipp did, of course, but 50 years ago, this was all new. In times of industrialization and chemical agriculture, Claus Hipp had already set a counter - trend here, created a different model of thinking and thus hit the nerve of the coming decades to this day ", said the Minister, handing the prize over in her function as" Ecologia Ambassador of the Ecology 2017 "together with Hans-Joachim Ritter. The Chairman of the Foundation for Ecology and Democracy said in his speech: "Claus Hipp is a pioneer of ecological awareness in agriculture and society, a shining example of an entrepreneurial personality,
previous awards:Focus on the human being -
social and social responsibility
For HiPP, social responsibility is the essential basis for successful entrepreneurial action. This is reflected not only in the sustainable measures of personnel management, but also distinguishes the diverse social commitment in solidarity with people in need: HiPP helps young families with multiple births and regularly donates for the non-profit organization "Münchener Tafel e. V. ". Also auxiliary transport of Caritas in crisis areas supports HiPP. For the exemplary assumption of social responsibility HiPP 2013 received the first prize of the German Federal Government for Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR).
Since 1999, the company has its own ethics charter based on responsibility to people, nature and the environment. Central concerns are fair competition and the respectful treatment of business partners, suppliers, customers and employees. HiPP recognizes that a perfect and harmonious alignment of our goals with our actions is a constant challenge. We want to face this and continuously improve ourselves in this process
As a family-friendly company, HiPP promotes the compatibility of family and work. Almost every department has different working models with flexible working hours, which give parents better career development opportunities. In Pfaffenhofen alone, 200 individual models and flextime variants without core time are used. The fact that the workforce feels comfortable is shown by the comparatively long periods of service.
The health and well-being of employees is the highest asset of a company. Those who feel comfortable feel more quality of life, are happier, more balanced and also more committed. Occupational health management is becoming more and more important as a component of HR, quality and sustainability management. Occupational pensions, high standards of occupational safety and health, action days for health, fitness and sports activities promote the well-being of our workforce. Organic food, regional food and allergen management round out the commitment in the company restaurant. So vegetarian and vegan dishes are also firmly integrated into the diet.
Employees from over 20 different nations work at HiPP. We are especially proud of this cultural diversity. It enriches the corporate culture and strengthens our successful presence in the global environment.
 |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nutritional information | Ingredients | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The anlaysis values are subject to the usual variations in products made from natural products. Packed in a protective atmosphere. *Standard dissolution: 12.8 g HiPP Comfort Special Food + 90 ml water = 100 ml ready-to-drink food. 1 level measuring spoon = approx. 4.3 g HiPP Comfort Special Food |
Lactose, maltodextrin, vegetable oils (palm oil❤, rapeseed oil, sunflower oil), starch,beta-palmitate¹ (from palm oil and sunflower oil), hydrolyzed whey protein,galactooligosaccharides from lactose, calcium orthophosphates, emulsifier citric acid esters of mono- and diglycerides of fatty acids, potassium chloride, fish oil,choline, M. alpina oil, L-phenylalanine, L-tyrosine, potassium hydroxide, magnesium chloride,sodium citrate, sodium hydroxide, L-arginine, sodium selenite, L-tryptophan, calcium carbonate, L-histidine, zinc sulfate, calcium chloride, inositol, potassium iodate, ferrous sulfate,L-carnitine, vitamin E, Pantothenic acid, natural lactic acid cultures (Limosilactobacillus fermentum hereditum®)², niacin, copper sulfate, vitamin B1, vitamin A,vitamin B2, manganese sulfate, vitamin B6, metafolin®³ (calcium L-methylfolate), vitamin K, biotin, vitamin D, vitamin B12. 1Specially structured fat, based on the model of breast milk.
Important notes
|
When preparing infant milk formula, follow the instructions for use exactly. Improper preparation or storage of the prepared bottle over a longer period of time can lead to adverse health effects, e.g. due to the growth of undesirable germs. Therefore, prepare food freshly before each meal and feed immediately. Do not reuse leftover food. Thoroughly clean the bottle, teat and ring. Re-seal the opened pouch tightly after product removal, store in a dry place at room temperature and use within 3 weeks. Do not heat the food in the microwave (risk of scalding).
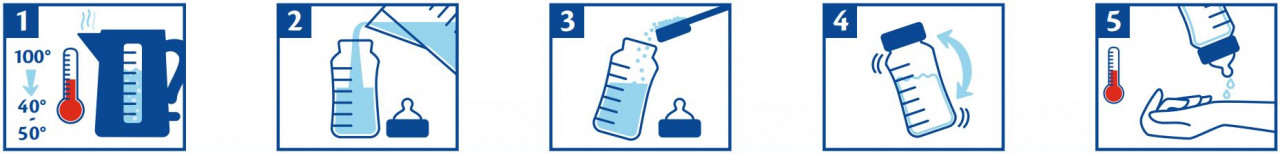

*To avoid damaging the natural lactic acid cultures (lactobacilli), please do not prepare food with water that is too hot.
Drinking amount per bottle may vary from individual to individual. Recommended amounts and number of bottles per day are guidelines. Your baby does not necessarily have to drink the entire bottle. Please use only the enclosed measuring spoon! 1 measuring spoon corresponds to 30ml of water.
| Age | Bottle meals per day | ready to drink food | boiled water | Measuring spoon |
| 1.-2. week* | 7-8 | 70 ml | 60 ml | 2 |
| 3.-4. week | 5-7 | 100 ml | 90 ml | 3 |
| 5.-8. week | 5-6 | 135 ml | 120 ml | 4 |
| 3.-4. month | 5 | 170 ml | 150 ml | 5 |
| 5. Month | 4-5 | 200 ml | 180 ml | 6 |
| from 6 month** | 4 | 235 ml | 210 ml | 7 |
* Unless otherwise recommended by the doctor. ** From the 5th month, you can start with jars and porridges in consultation with the pediatrician. Babies need approximately 5 meals per day. With each newly introduced jar and porridge meal, one bottle meal should be omitted.
 Many babies burp some food after a meal. This is completely normal and need not worry you as long as your little darling is doing well and growing and thriving. However, if your baby is burping or spitting up more often and you are concerned about his or her thriving, please contact your pediatrician. He or she can clarify whether a special food, such as HiPP Anti-Reflux Bio-Special Food, is appropriate for your little one.
Many babies burp some food after a meal. This is completely normal and need not worry you as long as your little darling is doing well and growing and thriving. However, if your baby is burping or spitting up more often and you are concerned about his or her thriving, please contact your pediatrician. He or she can clarify whether a special food, such as HiPP Anti-Reflux Bio-Special Food, is appropriate for your little one.
Carob bean gum is added to HiPP Anti-Reflux Organic Special Food. This natural swelling agent makes the food particularly creamy and ensures that it stays in the stomach better. This reduces reflux into the esophagus (anti-reflux). In principle, special foods should only be given under medical supervision.
Infants' intestines are still very sensitive in the first few months. This is why gastrointestinal complaints such as flatulence, colic or constipation are not uncommon. Experience has shown that digestive complaints can be managed well by being very close to your baby and keeping him or her calm during the day, by massaging the stomach and burping. Most of the time, these digestive problems go away on their own. In case of constipation, you should pay attention to the correct dosage of food when using an infant formula.
If your baby suffers increasingly from digestive problems coupled with excessive crying, a special food can help to alleviate the discomfort. Due to its special composition, HiPP Comfort special food has a digestion-regulating and stool-loosening effect and can therefore help with flatulence and constipation. You can find out whether HiPP Comfort special food is suitable for your baby after consulting your pediatrician. Special foods should only be given under medical supervision.
 In this case, both HiPP special foods should be considered differently:
In this case, both HiPP special foods should be considered differently:
If your child has digestive problems and spits up more at the same time, you should definitely discuss this with your pediatrician. He knows your baby and can best judge and decide which diet is best for your child. Usually, the digestive problems are the more urgent problem. However, this must be decided on a completely individual basis.
In principle, it is possible to feed HiPP special foods together with HiPP infant formula. Your pediatrician can decide whether this makes sense in individual cases and make an appropriate recommendation. It should be borne in mind that the relief of symptoms of flatulence, constipation or increased spitting up is brought about by the special composition of the foods in question.
In the case of a spitting-up baby, the particularly creamy HiPP Anti-Reflux Organic Special Food reduces the reflux of food into the esophagus. If a conventional infant formula is used at the next meal, this effect is then not present.